Typical design & specs
From lab-equipment suppliers you’ll see features like:
-
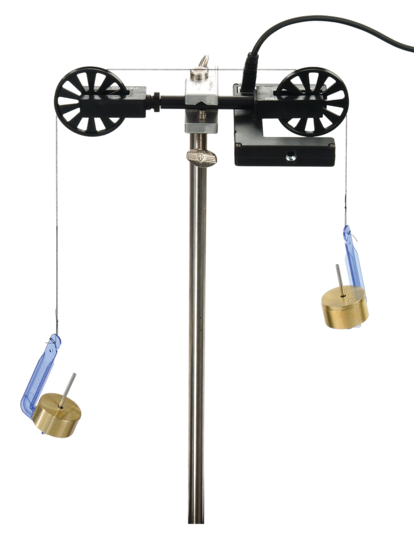
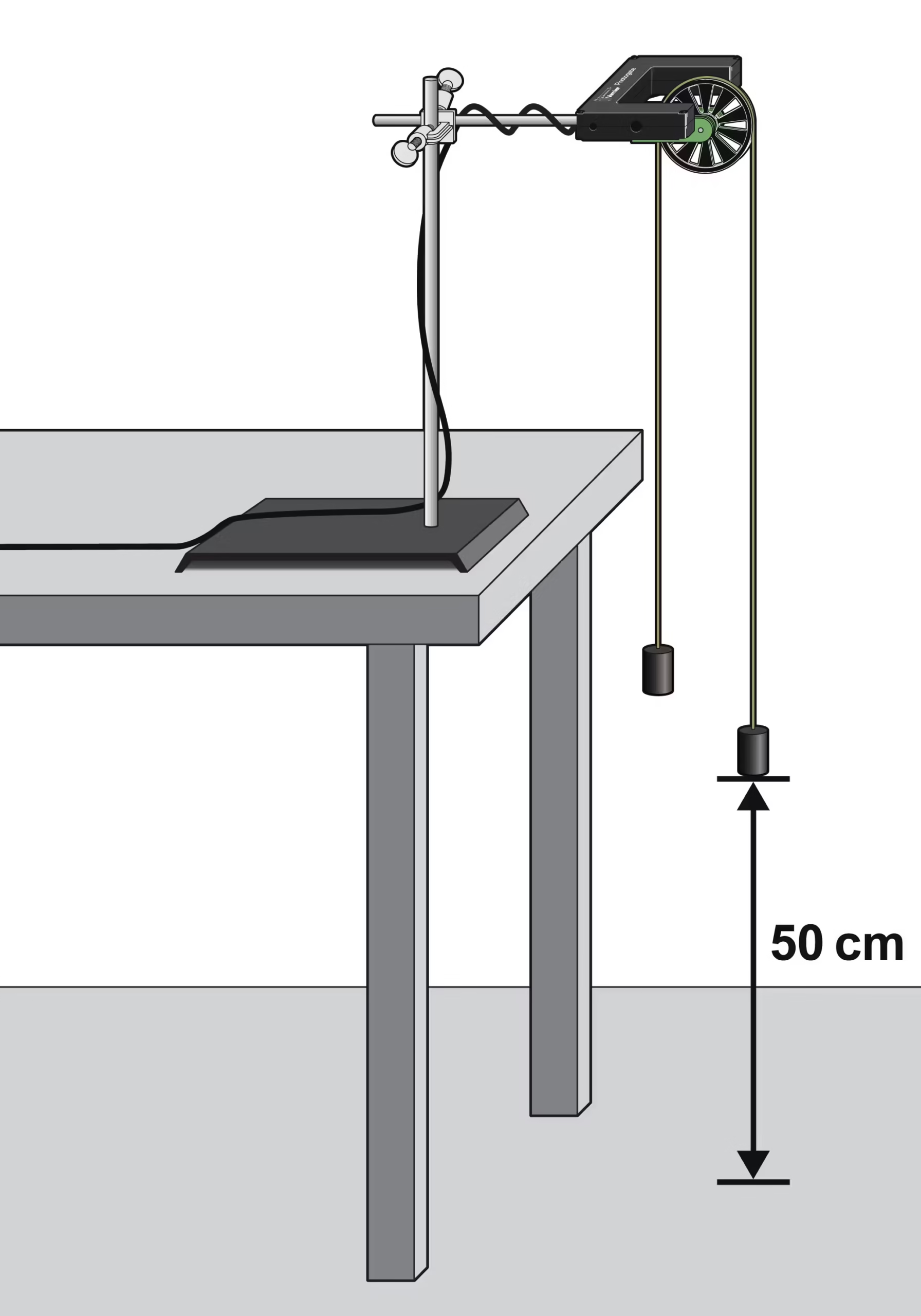
Two hanging masses connected by a light string over a low-friction pulley.
-
The pulley mount uses a rod and stand so the system can hang freely.
-
Pulleys often have ball bearings, minimal friction, and a known diameter. For example: one model uses two 50 mm (≈2″) ball-bearing pulleys connected by an aluminum rod.
-
On one model: Pulley diameter = 5.1 cm, moment of inertia ≈ 1.8×10⁻⁶ kg·m².
-
The string is massless (or as light as feasible), inextensible, and you hang different masses to vary the net force and total mass.
-
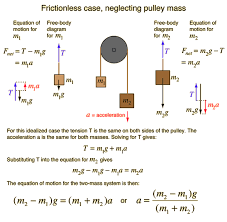
The apparatus is used to test acceleration: a=g (m2−m1)/(m1+m2)a = g\,(m_2 – m_1)/(m_1 + m_2) (ideal case) and more complex if pulley inertia/friction matter.